What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of an organization or project. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
SWOT analysis has its roots in the business world, where it has been used since the 1960s to help organizations assess their competitive position and develop strategies for growth. The concept was first introduced in a 1960 paper by management consultant Albert Humphrey.
The analysis involves examining internal factors, such as the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as external factors, such as market trends and competition. This allows organizations to identify areas where they excel and areas where they need improvement, as well as opportunities for growth and potential threats to their success.
One of the key benefits of SWOT analysis is that it provides a structured framework for evaluating an organization’s position and making informed decisions. By identifying strengths and weaknesses, organizations can better allocate resources and develop strategies to address areas that need improvement. Similarly, by identifying opportunities and threats, organizations can proactively respond to changes in the market and stay ahead of the competition.
SWOT analysis can be used in a variety of contexts, from evaluating a company’s overall position to assessing the viability of a specific project or initiative. It is a versatile tool that can be adapted to meet the needs of different organizations and industries.
Strengths
Strengths refer to the positive internal attributes or characteristics of an organization that give it a competitive advantage over others in its industry.
Identifying strengths is an important first step in a SWOT analysis because it helps organizations understand what they do well and what sets them apart from the competition. This information can be used to develop strategies that leverage those strengths and capitalize on them to achieve greater success. Strengths can come in many forms, such as:
- Brand recognition and reputation
- Unique products or services
- Strong financial position
- Highly skilled and motivated workforce
- Patented technology or intellectual property
- Strong customer relationships
- Efficient operations and supply chain management
Identifying strengths requires an honest and objective evaluation of an organization’s internal capabilities and resources. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of market research, as well as through internal analysis of financial and operational data.
Once strengths are identified, organizations can use them to their advantage by developing strategies that capitalize on those strengths. For example, a company with a strong brand and reputation may focus on increasing brand awareness through advertising and public relations campaigns. A company with patented technology may invest in research and development to create new products that leverage that technology.
Overall, identifying and leveraging strengths is a key component of successful strategic planning. By understanding what sets them apart from the competition, organizations can develop strategies that capitalize on their strengths and help them achieve their goals.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses refer to the negative internal attributes or characteristics of an organization that can hinder its ability to compete in its industry.
Identifying weaknesses is an important step in a SWOT analysis because it helps organizations understand what areas they need to improve in order to remain competitive. This information can be used to develop strategies that address those weaknesses and help the organization overcome them. Weaknesses can come in many forms, such as:
- Poor financial position or lack of resources
- Outdated technology or infrastructure
- Lack of brand recognition or reputation
- Inefficient operations or supply chain management
- Low employee morale or high turnover rates
- Inadequate marketing or sales strategies
- Lack of strategic partnerships or alliances
Identifying weaknesses requires an honest and objective evaluation of an organization’s internal capabilities and resources. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of market research, as well as through internal analysis of financial and operational data.
Once weaknesses are identified, organizations can develop strategies to address them. For example, a company with outdated technology may invest in new infrastructure or systems to improve its operations. A company with low employee morale may focus on improving its company culture or providing training and development opportunities.
Opportunities
Opportunities refer to the external factors or circumstances that can be leveraged by an organization to achieve its goals.
Identifying opportunities is an important step in a SWOT analysis because it helps organizations understand where they can focus their resources to achieve the greatest impact. This information can be used to develop strategies that capitalize on those opportunities and help the organization achieve its goals. Opportunities can come in many forms, such as:
- New market trends or emerging technologies
- Changes in regulations or government policies
- Shifts in consumer behavior or preferences
- Strategic partnerships or collaborations
- Acquisition or merger opportunities
- Changes in the competitive landscape
- Economic or industry growth
Identifying opportunities requires an understanding of the external environment in which an organization operates. This can be done through market research, industry analysis, and monitoring of trends and changes in the business environment.
Once opportunities are identified, organizations can develop strategies to take advantage of them. For example, a company operating in a growing industry may focus on expanding its product offerings to capitalize on the increased demand. A company with a strong reputation may use that reputation to build strategic partnerships with other organizations in its industry.
Threats
Threats refer to external factors or circumstances that may hinder or pose a risk to an organization’s ability to achieve its goals.
Identifying threats is crucial in developing effective strategies that mitigate potential negative impacts on the organization. Threats can come from a variety of sources, such as:
- Economic downturns or shifts in consumer spending
- New competitors or disruptive technologies
- Changes in regulations or government policies
- Shifting market trends or consumer preferences
- Natural disasters or other external events
To identify potential threats, organizations should conduct a thorough analysis of the external environment in which they operate. This can be done through market research, industry analysis, and monitoring of trends and changes in the business environment.
Once threats have been identified, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate their potential impact. For example, a company facing increased competition may focus on differentiating its products or services to maintain its market position. A company operating in a region prone to natural disasters may develop contingency plans to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster.
It is important to note that threats may not always be entirely negative. In some cases, they may present opportunities for growth or development. For example, a new competitor entering the market may prompt a company to innovate and improve its products or services to remain competitive.
How to Do a SWOT Analysis
As shown above, SWOT analysis can be a powerful tool. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform a SWOT analysis.
Step 1 – Define the objective: Determine the purpose of the analysis and what you hope to achieve. This will help guide your approach.
Step 2 – Gather information: Collect data on the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This may involve conducting market research, reviewing financial statements, or surveying employees.
Step 3 – Identify strengths: Determine what the company does well and what sets it apart from the competition. Consider factors such as the company’s reputation, brand recognition, and unique selling proposition.
Step 4 – Identify weaknesses: Determine what the company needs to improve on and where it may be falling behind the competition. Consider factors such as financial stability, employee turnover, and customer satisfaction.
Step 5 – Identify opportunities: Determine external factors that could benefit the company, such as emerging markets, changes in customer behavior, or advancements in technology.
Step 6 – Identify threats: Determine external factors that could harm the company, such as new competitors, changing regulations, or economic downturns.
Step 7 – Analyze the results: Review the data collected and identify patterns or trends. This will help you identify the most important factors and prioritize them for action.
Step 8 – Develop an action plan: Use the insights gained from the analysis to develop an action plan that addresses the identified issues. This may involve developing new products or services, improving internal processes, or investing in new technology.
Step 9 – Monitor and adjust: Regularly review and adjust the action plan as needed to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
By following these steps, businesses can use SWOT analysis to gain a deeper understanding of their market positions.
SWOT Analysis Example: Amazon
Now that we understand what SWOT is and the steps to perform it, let’s take a look at a SWOT analysis example. We’ll use Amazon for our example.
Strengths:
- Dominant market position in e-commerce and cloud computing.
- Strong brand recognition and customer loyalty.
- Diverse product and service offerings, including Amazon Prime, Alexa, and Amazon Web Services.
- Advanced logistics and supply chain management capabilities.
Weaknesses:
- Dependence on third-party sellers for a significant portion of sales.
- “Too big”; antitrust concerns in some markets.
- Known to compete against its own customers.
- Increasing competition from other e-commerce and cloud computing companies.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand for online shopping and cloud computing services.
- Expansion into new markets, particularly in emerging economies.
- Investment in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and drone delivery.
- Diversification into new industries, such as healthcare and entertainment.
Threats:
- Intense competition from other e-commerce and cloud computing companies.
- Increasing regulatory scrutiny and potential changes in tax laws.
- Economic downturns or shifts in consumer behavior that could impact sales.
- Potential supply chain disruptions or cybersecurity threats.
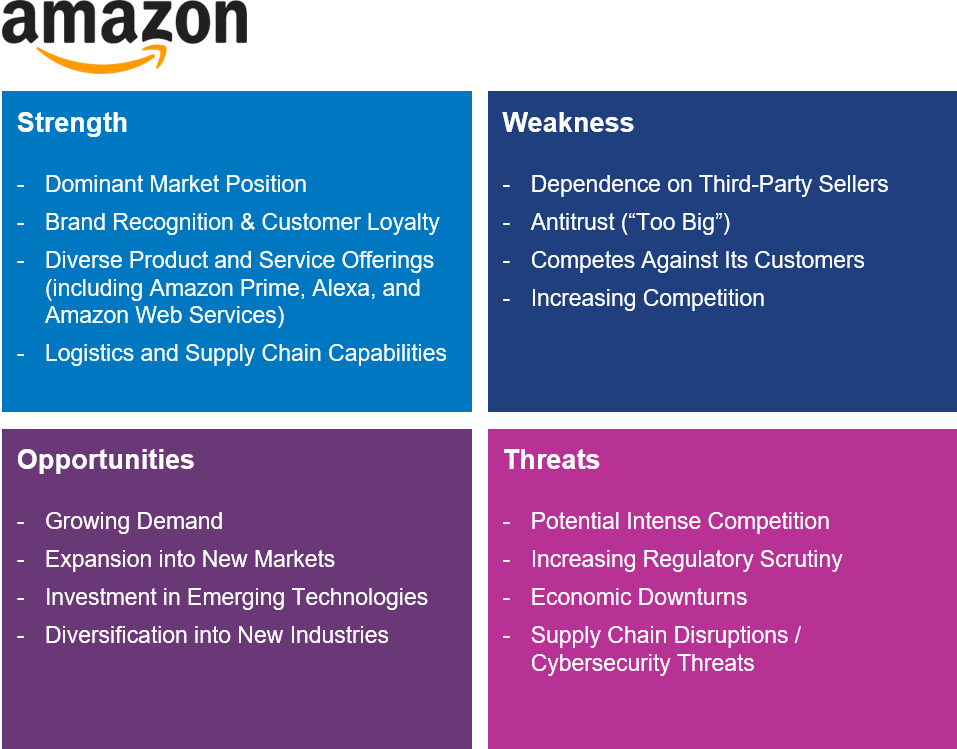
As we can see from this SWOT analysis of Amazon, the company has a number of strengths that have contributed to its dominant market position, including strong brand recognition, diverse product offerings, and advanced logistics capabilities. However, the company also faces several weaknesses, such as dependence on third-party sellers and criticism of labor practices.
SWOT Analysis Advantages & Disadvantages
One of the advantages of SWOT analysis is its simplicity. The technique is easy to understand and can be used by individuals at all levels of an organization. It also allows companies to quickly identify areas of strength and weakness, providing a starting point for further analysis and action. SWOT analysis is also versatile and can be used for a variety of purposes, such as evaluating a product or service, assessing a competitor, or analyzing an industry.
However, there are also disadvantages to using SWOT analysis. One of the main limitations is its potential to oversimplify complex situations, failing to provide nuanced insights. Results may be influenced by personal biases or incomplete information, and the analysis may be limited in scope, failing to account for important factors. Furthermore, SWOT analysis does not prioritize or rank the identified factors, making it difficult to determine which issues are most important to address. Finally, it may not provide clear guidance on how to take action based on the analysis.
Despite these limitations, SWOT analysis remains a popular and valuable tool for companies seeking to evaluate their business environment and make strategic decisions. To make the most of SWOT analysis, companies should ensure they have a diverse team of stakeholders involved in the process and use it in conjunction with other analytical tools to gain a more complete understanding of their situation.
Learn Finance to Support SWOT Analysis
At Lumovest, we’re building the place where anyone can learn finance and investing in an affordable and easy-to-understand manner. Our courses are far more intuitive, visualized, logical and colloquial than your college professor-taught courses. Our courses are taught by Goldman Sachs investment banker who has worked on transactions worth over $50 billion. We designed our courses to prepare you to succeed in the world of high finance. You’ll learn how to conduct financial analysis exactly like how it’s done on Wall Street’s top firms. Upon completion of the courses, you will receive our Global Financial & Investment Analyst (GFIA) certification. You can sign up here.
