One curriculum to advance your career.
We have a curriculum that will help you develop the key skills you need to succeed in finance.
We have a curriculum that will help you develop the key skills you need to succeed in finance.
We developed our curriculum based on how work is done at the world’s top investment banks, private equity firms and hedge funds. We spent many years working at these firms and distilled everything we learned into a single curriculum to supercharge your career.
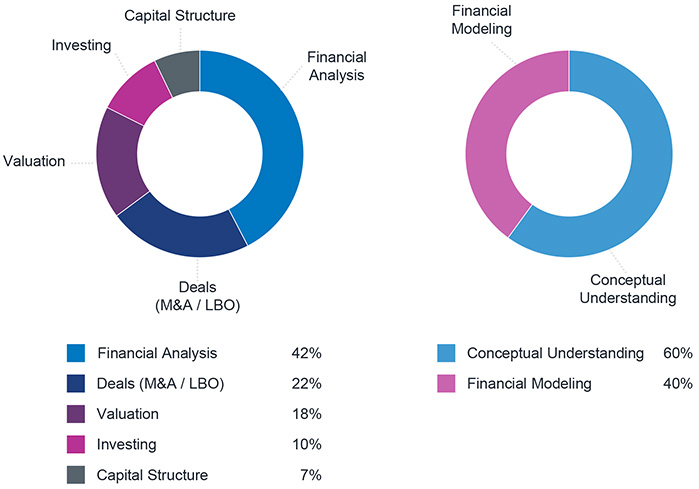
Conceptually, you’ll learn all the major topics in finance: Accounting, Valuation, Capital Structure, Transactions (M&A, LBO, etc), and Capital Markets. Practically, you’ll learn how to build dynamic and sophisticated financial models like how we do it on Wall Street.
Many job candidates for investment banking, private equity, hedge fund, corporate finance and other finance jobs try to memorize the answers to the common interview technical questions. Naturally, they struggle when the interviewers alter the questions a bit or throw them a curveball. Their answers are built on a weak technical foundation that could easily crumble and interviewers see right through it.
That’s why we emphasize logical flow in our curriculum. Once you understand the logic behind all the formulas and jargons, finance will make natural sense to you. You’ll be able to think through problems on the spot, which is a lot more impressive. No other institution’s curriculum is as good at showing you the logical flow behind finance as ours. Not even Harvard Business School.
As we progress through our courses, we’ll teach you how to build beautiful, dynamic and effective financial models using best practices as they’re taught to us during our Investment Banking Analyst days at Goldman Sachs. We’ll start simple and build up to more complex maneuvers in Excel as we progress.
Revenue is known as the “top-line” and it drives the rest of the financials. In our courses, we teach you to think about revenue and analyze it in terms of key drivers, which is how it’s done at the top private equity firms and hedge funds.
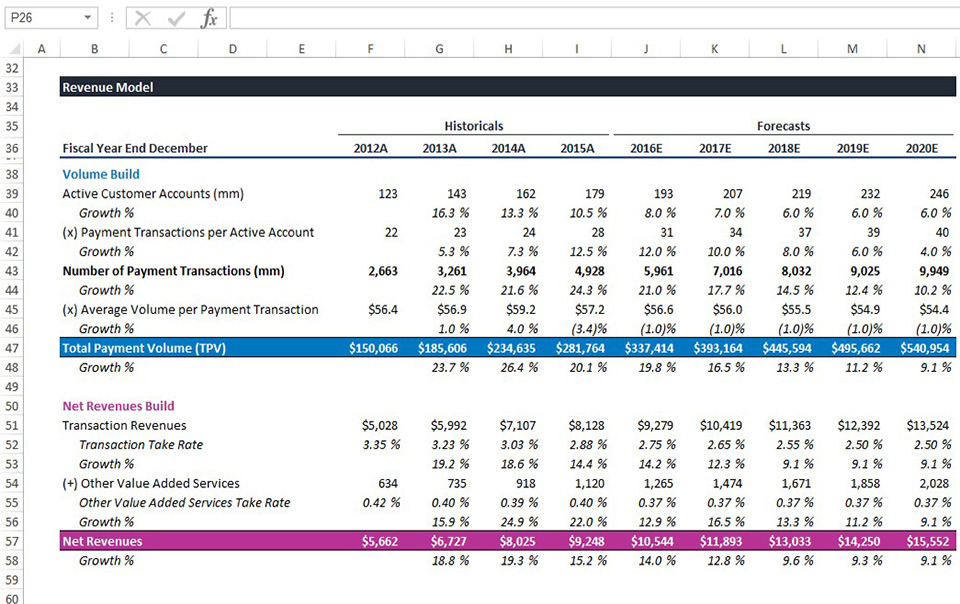
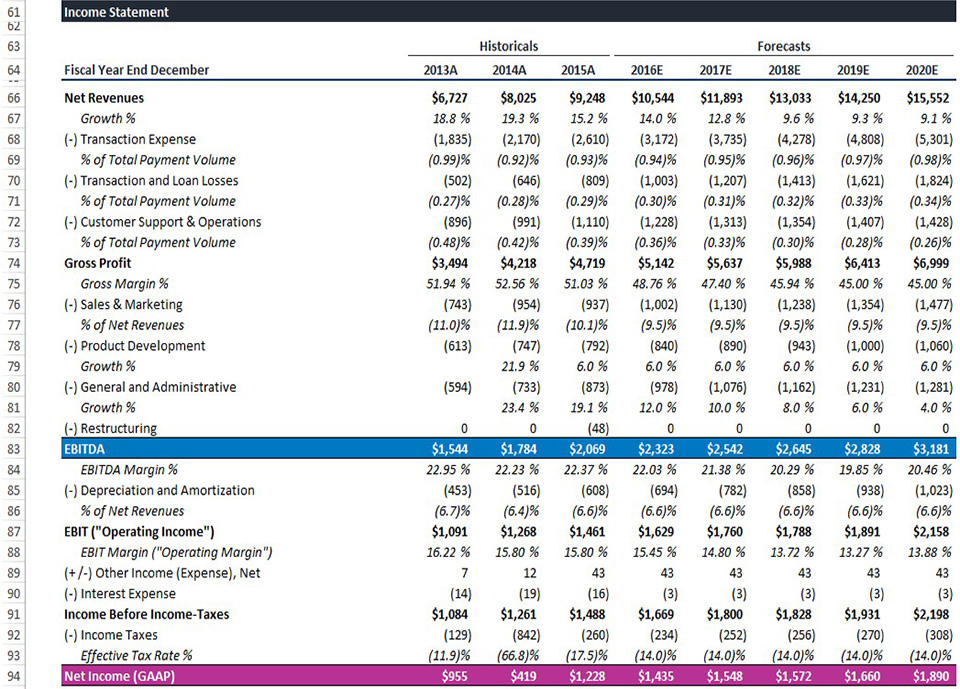
The operating model serves as the backbone on which you can layer on valuation and/or transaction models, such as DCF, M&A and LBO. Whether you’re working on the sellside or the buyside or in corporate, you’ll need to know how to analyze a company’s operating performance and model it. We’ll teach you how to build an operating model with GAAP and non-GAAP financials.
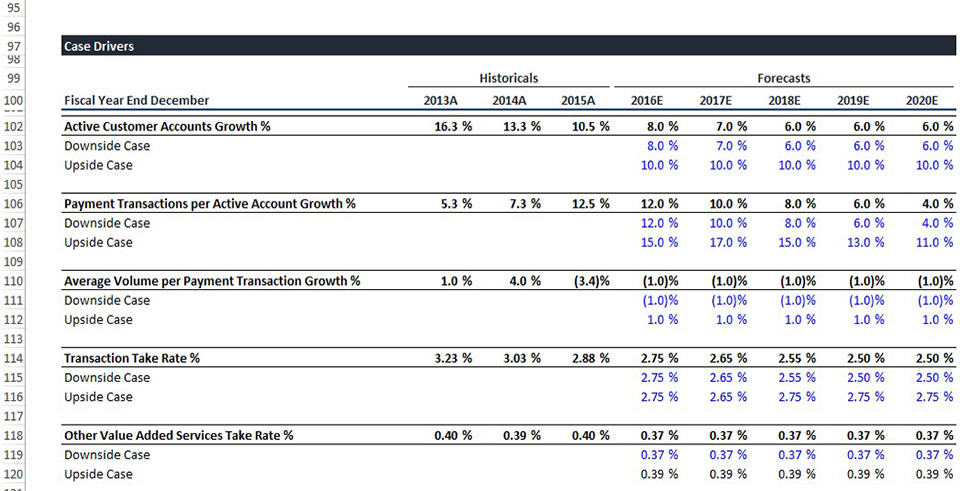
Learn how to efficiently build case drivers to reflect financials under different possible scenarios. You’ll be able to flex different scenarios at the click of a button. This becomes particularly relevant when analyzing a company’s performance under different potential outcomes.
1
This course goes over important stock basics and establishes the context for the investment analysis we’ll learn in the subsequent courses.
2
This course goes over the investor resources that we’ll utilize to analyze companies and stocks and where to find them.
3
Corporate Valuation is the cornerstone of financial analysis. It’s the framework that quantifies what a company is worth.
4
Revenue Model relates to how businesses generate revenue. We’ll learn how companies recognize revenue and how to analyze it.
5
Cost Structure refers to the composition of the different types and characteristics of the expenses incurred by a company.
6
Earnings Power refers to the business’s ability to generate profits. We’ll learn the different measures of profits and what they represent.
7
Cash Flow is the movement of cash into and out of the company. A company’s value is based on how much cash flow it can generate.
8
Intrinsic Valuation is the process of determining the intrinsic value of a company by analyzing how much cash it will generate.
9
Risk Reward relates to the evaluation of the potential for gains and losses of an investment opportunity.
10
Balance Sheet is one of the 3 major financial statements. It shows what the company owns and what it owes.
11
Working Capital is an important element of every business and it appears on both the Balance Sheet and the Cash Flow Statement.
12
This course explores how the Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and the Balance Sheet are interlinked.
13
Valuation Multiples are ratios that measure how many times or “turns” investors are willing to pay for every dollar the company earns.
14
A Buyout is the purchase of all or substantially all of a company and obtaining control over it through the process.
15
Capital Structure refers to the composition of debt and equity in a company. Debt and equity are capital that finance every company.
16
Leveraged Buyout (LBO) is the purchase of all or substantially all of a company using a large amount of debt.
17
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) plays a critical role in finance. It’s the subject of companies buying and selling other companies.
18
This is a financial modeling course where we will learn how to build a full-blown 3-statement operating model.