What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that helps businesses improve their processes to maximize the quality of their products and services while minimizing defects.
In other words, Six Sigma is a method to manage product / service quality. The ultimate goal of Six Sigma is to achieve a level of quality that meets or exceeds customer expectations while minimizing costs and maximizing profits.
Implementing this method can lead to numerous benefits for businesses, including improved quality and efficiency, reduced costs, increased customer satisfaction, and higher profitability. By focusing on data and process improvement, businesses can achieve greater consistency and predictability in their operations. It also encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve their processes and stay ahead of the competition.
By using Six Sigma, businesses can identify areas for improvement and measure progress towards achieving their goals. In this article, we will discuss the key principles of Six Sigma, its benefits, and how it can be implemented in business.
Six Sigma Methodology
Six Sigma methodology is a data-driven approach that relies on statistical analysis to identify areas for improvement and measure progress towards achieving process improvement goals. This methodology is focused on reducing the variability and defects of the business processes. The methodology consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC). The key activities of each phase are discussed below.
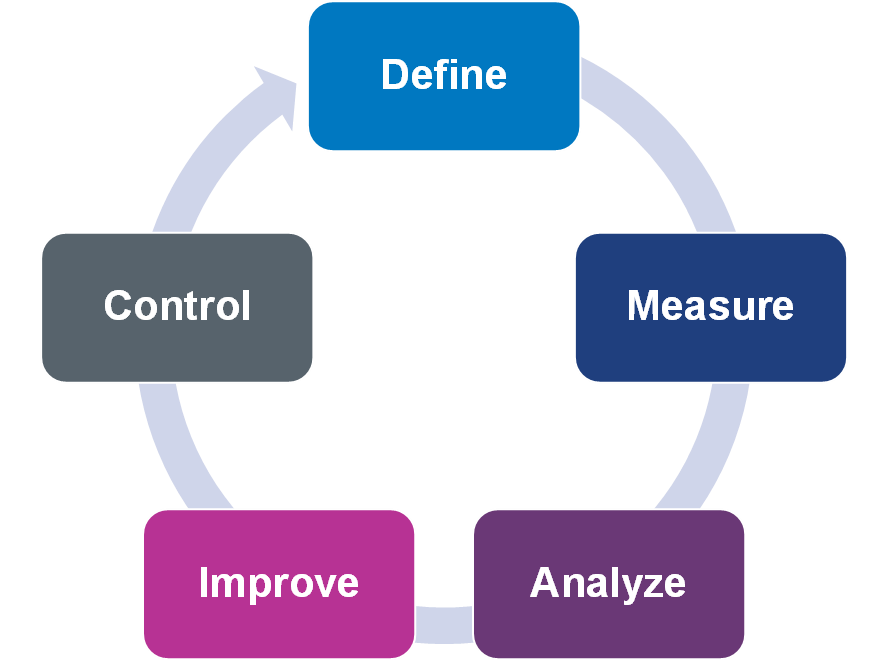
The Define phase is the starting point of the methodology. In this phase, businesses identify the problem they want to solve, define the scope of the project, and establish a team to work on the project. This team is responsible for managing the project and implementing the changes that will be required to achieve the desired outcomes.
The Measure phase is focused on collecting data on the process being evaluated. This data is then used to establish a baseline for performance, which will be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the process improvement efforts.
The Analyze phase involves analyzing the data collected in the previous phase to identify root causes of defects and inefficiencies in the process. In this phase, businesses use statistical tools to identify the most significant factors affecting the process and prioritize their improvement efforts accordingly.
The Improve phase involves developing and implementing solutions to address the root causes identified in the Analyze phase. This phase is focused on identifying and testing potential solutions, and then implementing the best solution to achieve the desired outcomes.
The Control phase involves monitoring the process to ensure that the improvements made in the Improve phase are sustained over time. This phase includes ongoing monitoring, auditing, and refinement of the process to ensure that it continues to deliver the desired outcomes.
Implementing Six Sigma
Implementing Six Sigma requires a commitment from all levels of the organization, from top management to frontline employees. Businesses must also provide appropriate training and support to ensure successful implementation. Training typically involves classroom instruction, hands-on projects, and mentoring from experienced professionals.
Implementing Six Sigma can lead to numerous benefits for businesses, including improved quality and efficiency, reduced costs, increased customer satisfaction, and higher profitability. By focusing on data and process improvement, businesses can achieve greater consistency and predictability in their operations. Six Sigma also encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve their processes and stay ahead of the competition.
Real World Example: Ford Motor
Ford Motor Company is a well-known example of a business that has successfully implemented Six Sigma. In the early 2000s, Ford faced numerous challenges related to quality, efficiency, and profitability. The company’s processes were plagued by defects, inefficiencies, and waste, which led to high costs, low customer satisfaction, and declining profits.
To address these challenges, Ford adopted Six Sigma as a key part of its quality management program. The company launched a comprehensive initiative aimed at identifying and eliminating defects in its processes.
One of the most significant improvements Ford achieved through Six Sigma was in its manufacturing processes. By applying Six Sigma methodologies to its production lines, the company was able to reduce defects, minimize waste, and increase efficiency.
Another area where Six Sigma had a significant impact on Ford was in its supply chain management. By using Six Sigma to improve its procurement processes, Ford was able to reduce lead times, increase on-time deliveries, and reduce costs. This helped the company to become more competitive and better able to meet customer demand.
Ford’s commitment to Six Sigma also had a positive impact on its workforce. By providing employees with Six Sigma training, the company was able to create a culture of continuous improvement, where employees were encouraged to identify and solve problems. This led to increased employee engagement, higher productivity, and improved morale.
In conclusion, Ford’s adoption of Six Sigma played a key role in its turnaround in the early 2000s. By using Six Sigma to identify and eliminate defects in its processes, the company was able to improve quality, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction. Through its commitment to Six Sigma, Ford was able to create a culture of continuous improvement that helped it to stay ahead of the competition and achieve long-term success.
Real World Example: Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP)
Another example of Six Sigma in the healthcare industry is the case of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP). CHOP is a leading pediatric hospital that provides a wide range of services, including primary care, specialty care, and research.
In 2007, CHOP launched a Six Sigma initiative aimed at improving patient care and reducing costs. The hospital faced numerous challenges related to patient wait times, patient flow, and staff efficiency, which led to high costs and long wait times for patients.
By using Six Sigma methodologies, CHOP was able to identify areas for improvement and implement solutions that resulted in significant improvements in patient care and efficiency. For example, the hospital used Six Sigma to streamline patient flow, reduce wait times, and improve patient satisfaction.
One of the key improvements CHOP achieved was in its radiology department. By using Six Sigma tools to analyze the radiology process, the hospital was able to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that were causing long wait times for patients. The hospital implemented a new process that reduced wait times by 30%, increased patient satisfaction, and reduced costs.
CHOP also used Six Sigma to improve its discharge process, which had been a major source of patient complaints. By analyzing the discharge process, the hospital was able to identify root causes of delays and develop a new process that reduced patient wait times and increased efficiency.
The Six Sigma initiative at CHOP had a significant impact on patient care and efficiency, leading to higher patient satisfaction, lower costs, and improved outcomes. The hospital was able to create a culture of continuous improvement, where staff were encouraged to identify and solve problems, leading to sustained improvements over time.
Six Sigma Belt Rankings
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement that relies on a team of experts with different levels of expertise. These experts are known as Six Sigma Belt holders and are categorized into different levels based on their skills and knowledge.
There are five Six Sigma belt levels: White Belt, Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Each belt level represents a different level of expertise, with higher belt levels indicating greater experience and knowledge.
- White Belt: The White Belt level is the entry-level belt and is designed for individuals who are new to Six Sigma. White Belt holders have a basic understanding of Six Sigma concepts and tools and can contribute to improvement projects.
- Yellow Belt: The Yellow Belt level is the next level up and is designed for individuals who have a basic understanding of Six Sigma concepts and tools. Yellow Belt holders work on improvement projects and assist Green Belt and Black Belt holders.
- Green Belt: The Green Belt level is the intermediate level and is designed for individuals who have a solid understanding of Six Sigma and can lead improvement projects. Green Belt holders work under the supervision of Black Belt holders and can lead small-scale Six Sigma projects.
- Black Belt: Black Belt holders are experts in Six Sigma and are able to lead complex projects and train others in Six Sigma methodologies. They have a deep understanding of Six Sigma tools and techniques and are able to analyze data to identify process improvements.
- Master Black Belt: The highest level of Six Sigma expertise is the Master Black Belt level. Master Black Belts are the most experienced Six Sigma practitioners and are responsible for leading large-scale Six Sigma initiatives, mentoring Black Belts, and coaching other Six Sigma professionals.
Learning Six Sigma
Certifications: There are several certification programs available, such as ASQ and IASSC. Each program has different requirements and levels of certification, such as White Belt, Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt.
Time Commitment: The estimated time requirement for each belt level may vary depending on the certification program and the individual’s pace of learning. However, here is a general estimation of the time required for each belt level.
- White Belt: This is the entry-level certification and can typically be completed within a day or two.
- Yellow Belt: This level requires a basic understanding of Six Sigma concepts and can take a few days or weeks to complete.
- Green Belt: This intermediate level requires more in-depth knowledge and can take several weeks to a few months to complete.
- Black Belt: This level requires expertise in Six Sigma methodologies and can take several months to a year to complete.
- Master Black Belt: This is the highest level of certification and can take several years to achieve, as it requires significant experience and expertise in leading large-scale Six Sigma projects.
It’s important to note that these time estimates are general and can vary depending on the certification program and the individual’s pace of learning. Some certification programs may require more or less time, and some individuals may take longer or shorter to complete each level depending on their experience and dedication.
Learning More
At Lumovest, we’re building the place where anyone can learn finance and investing in an affordable and easy-to-understand manner. Our courses are far more intuitive, visualized, logical and colloquial than your college professor-taught courses. Our courses are taught by Goldman Sachs investment banker who has worked on transactions worth over $50 billion. We designed our courses to prepare you to succeed in the world of high finance. You’ll learn how to conduct financial analysis exactly like how it’s done on Wall Street’s top firms. Upon completion of the courses, you will receive our Global Financial & Investment Analyst (GFIA) certification. You can sign up here.